C++ Compilation Process
In C++, a program foes from text files (or source files) to processor instructions as follows:
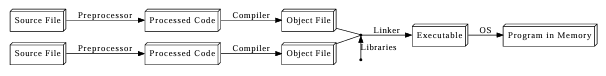
Summary
- Source files go through the C++ preprocessor
- The processed code goes through the compiler and converted into object files
- The object files are linked together along with libraries
- The output is the executable
Description
Object files are intermediate files that represent an incomplete copy of the program: each source file only expresses a piece of the program, so when it is compiled into an object file, the object file has some markers indicating which missing pieces it depends on.
The linker takes those object files and the compiled libraries of predefined code that they rely on, fills in all the gaps, and spits out the final program, which can then be run by the operating system.
The compiler and linker are just regular programs. The step in the compilation process in which the compiler reads the file is called parsing.