Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Background
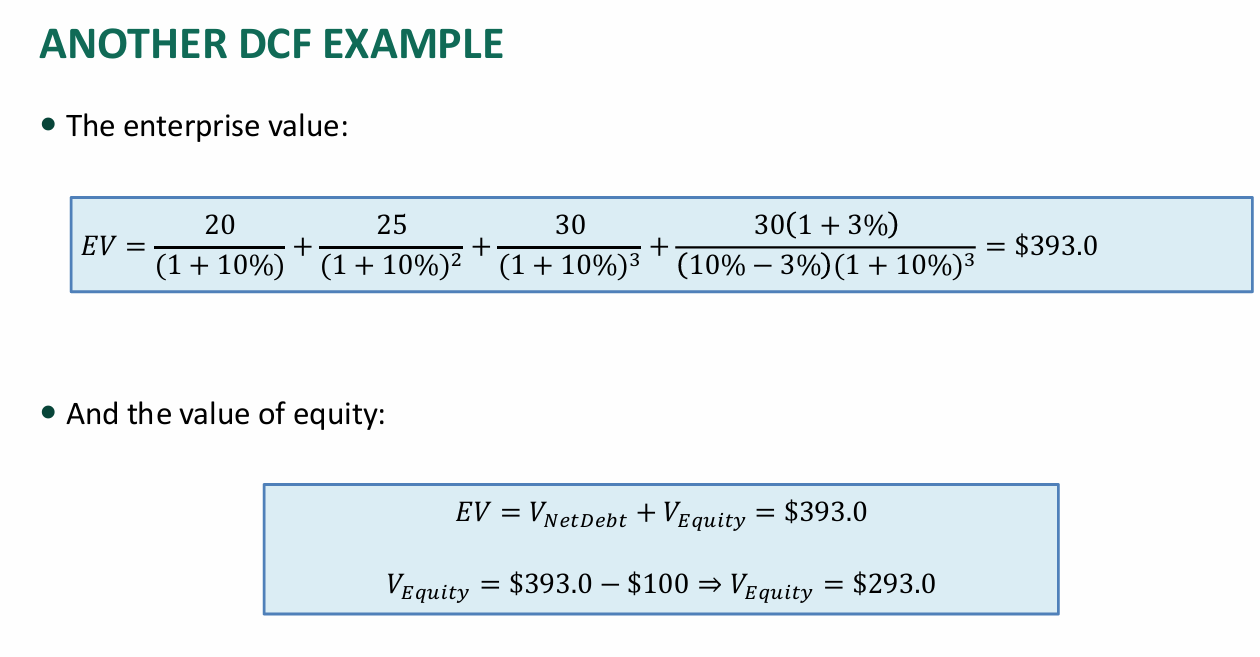
The value of a firm is the sum of the value of its equity and value of its debt. This is also the sum of the Enterprise Value and cash and cash equivalents.
Where:
- Net Debt = Total Debt - Cash and Cash Equivalents
DCF Steps
- Identify Free Cash Flows to the Firm (FCFF)
- Recognize time value of money
Using this, we can calculate the Enterprise Value.
Free Cash Flows to the Firm (FCFF)
Free Cashflow to the Firm represents cash flows to which all stakeholders (providers of capital) make claim. That is:
So FCFF is the Net Operating Profit After Tax, then we add back depreciation which is non-cash, subtract any investments into long-term assets, and subtract investments in short-term assets.
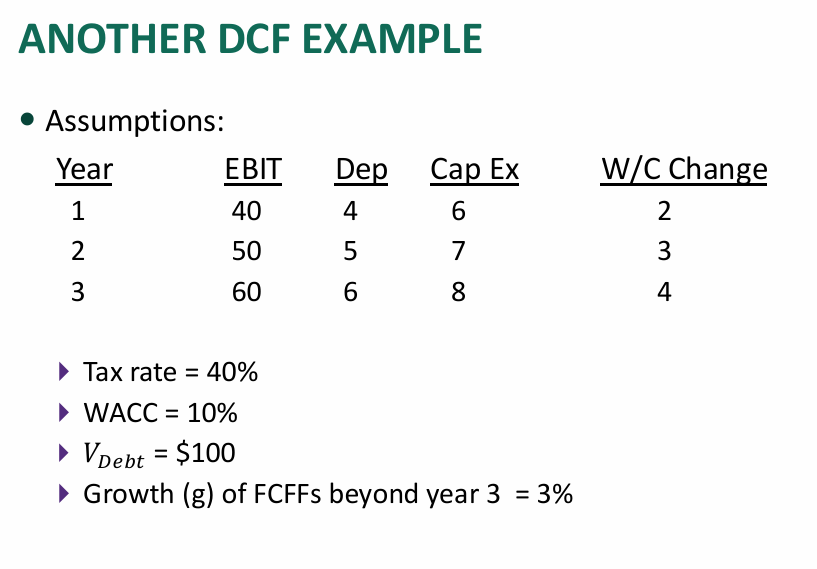
Example
Valuation of MatureCorp
- Find , , and price per share
- Firm has $200,000 in debt @ an interest rate of 10% per year
- There are 100k shares outstanding
- Tax rate is 40%
- Firm is at a very mature stage. Thus:
- It expects to generate $220,000 EBIT in perpetuity (all earnings are paid as dividends → no reinvestment)
- Future capital expenditures offset depreciation
- No future additional working capital investments are required
- WACC is 13.2%
Solution
- Calculate FCFF
- FCFF is constant in perpetuity
- Fair value of equity
- Price per share
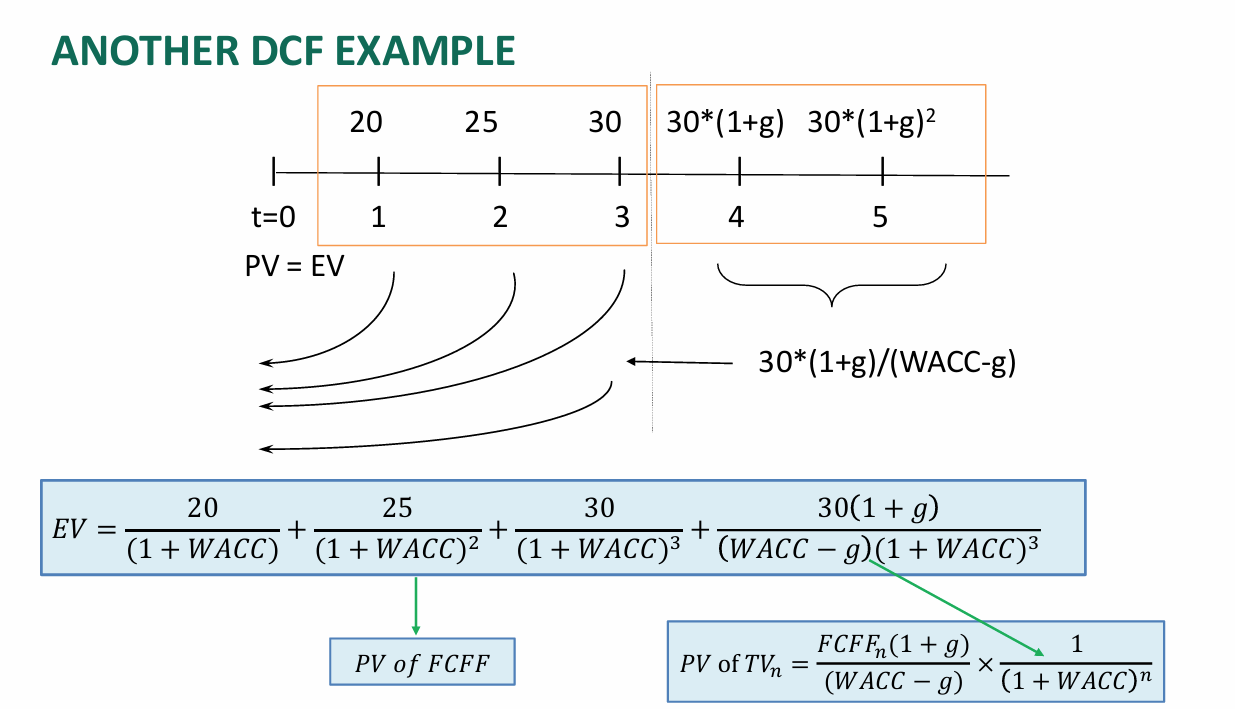
Two-Stage
Similar to Dividend Discount Model, we can also split the DCF into two stages:
Present value of Stage 1
Present value of Stage 2
Using this two-stage approach
Example