Orthogonal Projection
In linear algebra, an orthogonal projection is a linear transformation which maps a vector to a vector space such that the difference between the original vector and the projected vector is orthogonal to the vector space.
More formally, we can define a projection of onto a subspace of written as
where and is orthogonal to every vector in . This is written as
In human terms, is the vector in that is closest to .
Geometric Interpretation
Geometrically, the orthogonal projection of a vector onto a subspace can be visualized as dropping a perpendicular from the tip of to the subspace . The point where this perpendicular intersects is the projected vector .
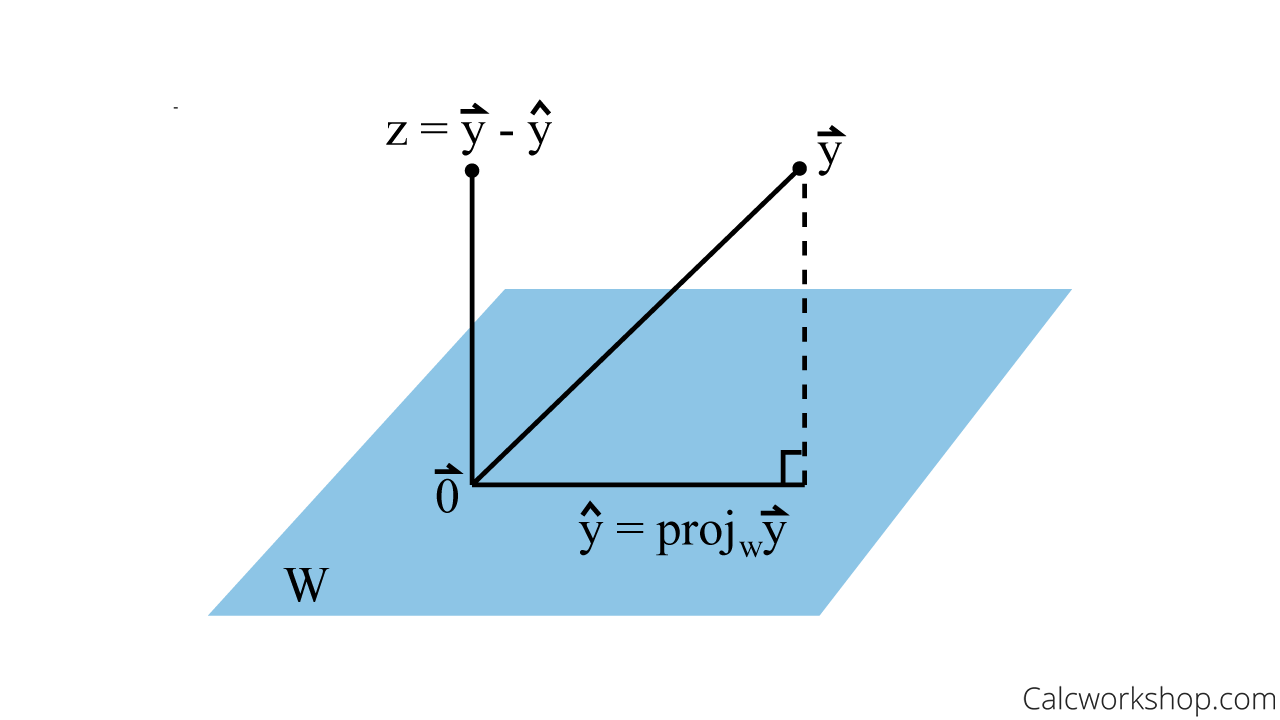
Examples
Example 1
Consider two vectors
Then we can say that and are orthogonal vectors as . We then define a subspace and an orthogonal basis for as:
Now our task is to find given
We start by calculating using the formula for projection onto an orthogonal basis:
Calculating the dot products:
Therefore
should then be an orthogonal vector to both and every element of .