HBA1 Finance Course
“Finance” course, taught in the first term of HBA1.
Exams - Final
- Concepts Covered:
- Focus is on second half of the course
- Previous concepts remain important (Time Value of Money, Capital Structure, Financial Ratios, Growing Perpetuities)
Module 4: The Cost of Capital
Module 5: Valuing Long-Term Investments and Businesses
Acquisition
- The acquirer refinances the target’s debt, and therefore the cost of debt changes to the buyer’s cost of debt.
Exams - Midterm
Module 1: Time Value of Money
Lecture: Time Value of Money
Primer
Note: below information is all duplicates of their respective notes. There exists atomic notes for all concepts including mathematical formulas and documentation on excel functions.
| Concept | Mathematical Formula (inline) | Excel Function |
|---|---|---|
| Future Value | • PV = present value • r = required rate of return • n = number of periods | =FV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type]) • rate = required rate of return • nper = number of periods • pmt = recurring payment amount • pv = present value |
| Present Value | • FV = future value • r = required rate of return • n = number of periods | =PV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type]) • rate = required rate of return • nper = number of periods • pmt = recurring payment amount • fv = future value |
| Net Present Value | • = cash flow in a given period • r = required rate of return | =NPV(rate, value1, value2, …) • rate = required rate of return • values = undiscounted future cash flows (starting in period 1) |
| Internal Rate of Return | No closed-form expression (cannot be calculated analytically). | =IRR(values) • values = undiscounted cash flows beginning at time zero |
Module 2: Financial Markets and Alternatives to Raising Capital
There is a lot of content here, but the main concepts are:
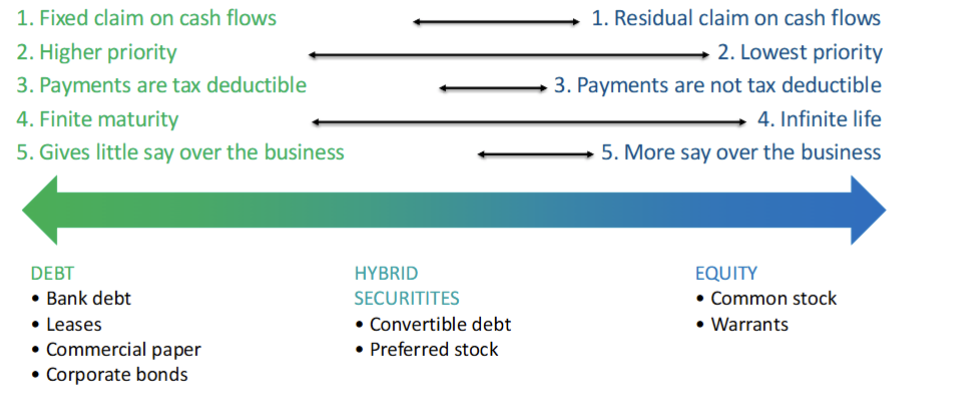
Additionally, we have some extra information here regarding terms:
Bonds vs. Stocks
Bonds:
- Fixed obligations
- Payment structure is generally known when issued.
- Indirect control only through debt contract terms
- Relatively high priority in bankruptcy
Stocks
- Residual claim on the firm
- No guarantee of dividends or return of capital
- Lowest priority in bankruptcy
- Voting control
Equity
We also note a important strategy Dividend Discount Model